Status Quo's Ric: Understanding Its Impact And Implications
Status Quo's Ric has become a pivotal concept in various fields, especially in economics and political theory. As we delve deeper into this topic, it is essential to grasp what "Ric" stands for and how it influences our current societal structures. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of Status Quo's Ric, its historical background, and its implications on contemporary issues. We will also discuss various perspectives surrounding this concept and provide insights that can aid in understanding its relevance today.
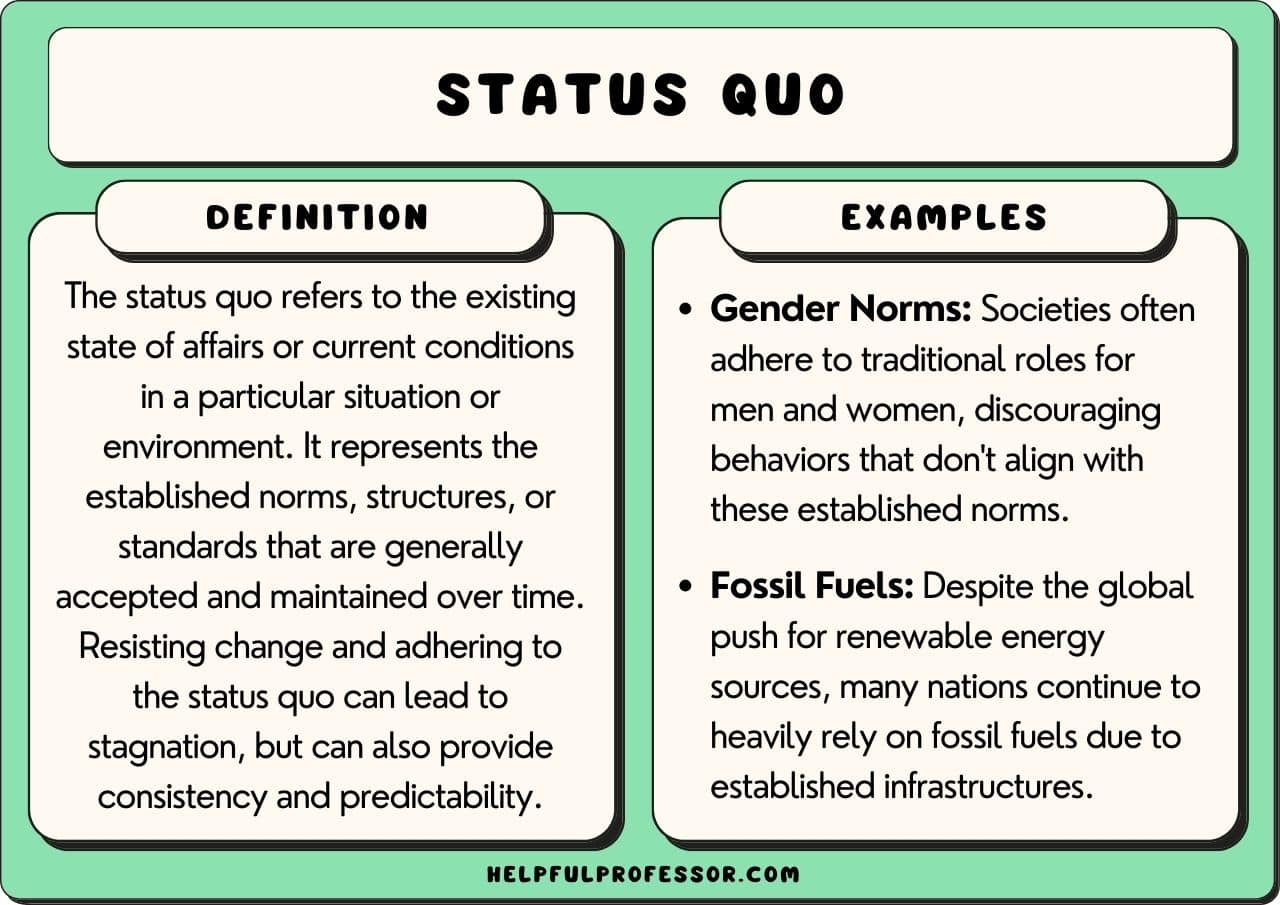
The term "Status Quo's Ric" is derived from the broader understanding of the term "status quo," which generally refers to the existing state of affairs. When combined with "Ric," which may refer to several theories or individuals in the economic realm, it creates a rich landscape for discussion. The intersection of these concepts often leads to debates on power dynamics, economic policies, and social structures. Thus, it is crucial to unpack these ideas carefully.
In the following sections, we will break down the various components of Status Quo's Ric, examining its historical context, its implications in modern society, and the debates that surround it. By the end of this article, readers should have a comprehensive understanding of the topic and its significance in today's world.
Table of Contents
- 1. Historical Context of Status Quo's Ric
- 2. Economic Theories Behind Ric
- 3. Societal Implications of Status Quo's Ric
- 4. Political Perspectives on Status Quo's Ric
- 5. Case Studies Illustrating Status Quo's Ric
- 6. Debate and Controversy Surrounding Status Quo's Ric
- 7. Future Outlook on Status Quo's Ric
- 8. Conclusion
1. Historical Context of Status Quo's Ric
Status Quo's Ric has roots in various historical movements and theories. To understand its impact today, it is important to look back at its evolution over time. The term "status quo" has been employed in numerous contexts, often to describe the prevailing conditions in society.
Historically, the status quo has been both challenged and upheld by various groups. For instance, during the Enlightenment, philosophers like John Locke and Thomas Hobbes discussed the nature of governance and the social contract, questioning the existing power structures. This philosophical groundwork laid the foundation for modern political thought and economic theories, including those surrounding "Ric."
As we navigate through the 20th and 21st centuries, the concept of status quo has seen various interpretations, particularly in the realm of economic policies and governance. Understanding this historical context is essential for grasping the complexities of Status Quo's Ric today.
2. Economic Theories Behind Ric
The term "Ric" often refers to David Ricardo, a prominent economist known for his theories on comparative advantage and rent. Ricardo's insights have had a profound influence on economic thought and policy-making. His work provides a framework for understanding how resources are allocated and how different economic agents interact within the status quo.
2.1 Comparative Advantage
Ricardo introduced the principle of comparative advantage, which suggests that nations should specialize in the production of goods where they have a lower opportunity cost. This principle has significant implications for international trade and economic policy, shaping the way countries engage in trade relations.
2.2 Rent Theory
Furthermore, Ricardo's theories on rent explain how landowners benefit from the economic activities on their land, reinforcing existing power structures. This aspect of his work highlights the relationship between economic factors and the status quo, illustrating how wealth can influence social dynamics.
3. Societal Implications of Status Quo's Ric
The implications of Status Quo's Ric extend beyond economics into societal realms. Understanding how these theories affect societal structures is vital for comprehending the current state of affairs.
3.1 Economic Inequality
One of the most significant societal implications of Status Quo's Ric is the perpetuation of economic inequality. As resources are concentrated among those who already hold wealth, the gap between different socioeconomic classes continues to widen.
3.2 Social Mobility
Furthermore, the status quo affects social mobility, as individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds often face barriers to advancement. The interplay between economic policies and societal norms can create cycles of disadvantage that are challenging to break.
4. Political Perspectives on Status Quo's Ric
Political ideologies play a crucial role in shaping the discourse surrounding Status Quo's Ric. Various political perspectives offer different interpretations of how the status quo should be maintained or challenged.
4.1 Conservative Viewpoints
From a conservative standpoint, maintaining the status quo is often viewed as essential for stability and order. Conservatives may argue that existing economic structures provide a foundation for prosperity and should not be disrupted.
4.2 Progressive Perspectives
In contrast, progressive viewpoints often advocate for reforming the status quo to address issues of inequality and injustice. Progressives argue that systemic changes are necessary to create a more equitable society.
5. Case Studies Illustrating Status Quo's Ric
To further understand the implications of Status Quo's Ric, examining case studies can provide valuable insights. These real-world examples illustrate how theoretical concepts manifest in practice.
5.1 Case Study: The New Deal
The New Deal, implemented in the United States during the Great Depression, serves as a significant case study. It challenged the existing economic status quo by introducing reforms aimed at providing relief, recovery, and reform. The policies enacted during this period aimed to redistribute wealth and address the economic inequalities exacerbated by the Great Depression.
5.2 Case Study: Globalization
Another relevant case study is globalization, which has reshaped economic relations worldwide. While globalization has created opportunities for growth, it has also reinforced existing inequalities, particularly between developed and developing nations. Understanding how globalization interacts with Status Quo's Ric is essential for grasping contemporary economic dynamics.
6. Debate and Controversy Surrounding Status Quo's Ric
The discourse surrounding Status Quo's Ric is rife with debate and controversy. Different stakeholders often have conflicting views on the implications and desirability of the current state of affairs.
6.1 Economic Policies Debate
One area of contention is the effectiveness of current economic policies. Critics argue that existing policies disproportionately favor the wealthy, perpetuating the status quo. In contrast, proponents may argue that these policies are necessary for maintaining economic stability.
6.2 Social Movements
Social movements advocating for change often challenge the status quo by highlighting issues of injustice and inequality. These movements play a crucial role in shaping public discourse and influencing policy decisions.
7. Future Outlook on Status Quo's Ric
Looking ahead, the future of Status Quo's Ric remains uncertain. The ongoing debates surrounding economic policies, social justice, and political ideologies will undoubtedly shape the trajectory of this concept.
As society grapples with pressing issues such as climate change, technological advancements, and global inequality, the need for reevaluating the status quo becomes increasingly apparent. Future discussions must consider the diverse perspectives that influence the understanding of Status Quo's Ric and its implications.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, Status Quo's Ric is a multifaceted concept that intersects with economics, politics, and societal structures. By examining its historical context, economic theories, societal implications, and political perspectives, we gain a comprehensive understanding of its relevance today.
As we move forward, it is essential to engage in constructive dialogues about the status quo and consider how it can be reformed for the betterment of society. We invite readers to share their thoughts on this topic, engage in discussions, and explore further readings on related subjects.
Thank you for taking the time to explore Status Quo's Ric with us. We hope this article has provided valuable insights and encourages you to return for more informative content in the future.
Article Recommendations
- Krystal Shanahan
- Frankie Muniz And Wife
- Takeoff Rapper
- La La Anthony And Carmelo
- Tammy Bradshaw
- Chloe Bennet And Logan Paul Back Together
- Real Erik And Lyle Family
- Good Morning Show Season 4
- The Twilight Saga Where To Watch
- Glenn Close Kids